Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体
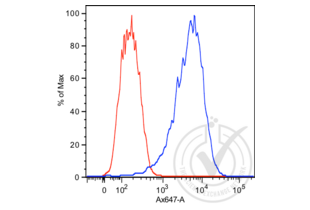
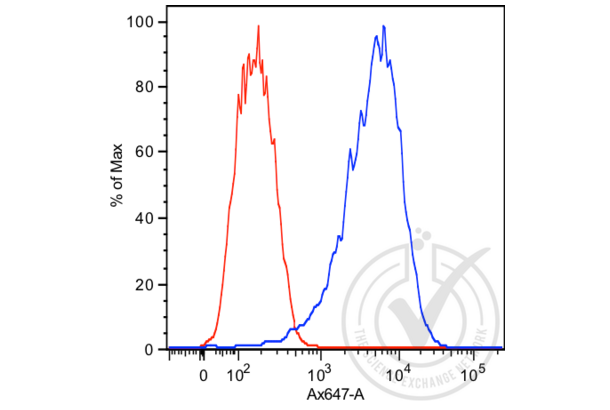 Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 (ABIN1543584)
Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 (ABIN1543584)
PSA 适用: 人 ELISA, WB, FACS, DB 宿主: 小鼠 Monoclonal A5D5-1 unconjugated
PSA 适用: 人 WB, IHC, IF, IP 宿主: 兔 Polyclonal unconjugated
PSA 适用: 人 ELISA, IHC, FACS 宿主: 小鼠 Monoclonal 5A11E2 unconjugated
Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 by Grade
Find Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 with a specific Grade. The Grade listed below are among those available. Click on a link to go to the corresponding products.
Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 by 适用
Find Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 for a variety of species such as anti-Human Prostate Specific Antigen, anti-Mouse Prostate Specific Antigen, anti-Rat Prostate Specific Antigen. The species listed below are among those available. Click on a link to go to the corresponding products.
Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 by 抗体来源
Find Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 with a specific 抗体来源. The 抗体来源 listed below are among those available. Click on a link to go to the corresponding products.
Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 by 克隆形成能力
Find available monoclonal or polyclonal Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体. Click on a link to go to the corresponding products.
Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 by Fragment
Find Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体 with a specific Fragment. The Fragment listed below are among those available. Click on a link to go to the corresponding products.
Popular Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体
- (1)
- (5)
- (2)
- (4)
- (4)
- (3)
- (3)
- (3)
- (3)
- (2)
- (1)
- (2)
- (1)
- (2)
- (2)
- (2)
- (2)
- (2)
Latest Publications for our Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体
: "A concentration-dependent multicolor conversion strategy for ultrasensitive colorimetric immunoassay with the naked eye." in: Analytica chimica acta, Vol. 963, pp. 129-135, (2018) (PubMed).: "Spectrum-based and color-selective electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for determining human prostate specific antigen in near-infrared region." in: Talanta, Vol. 165, pp. 117-121, (2017) (PubMed).
: "Quantification of Cancer Biomarkers in Serum Using Scattering-Based Quantitative Single Particle Intensity Measurement with a Dark-Field Microscope." in: Analytical chemistry, Vol. 88, Issue 17, pp. 8849-56, (2016) (PubMed).
: "A microfluidic platform for high-throughput multiplexed protein quantitation." in: PLoS ONE, Vol. 10, Issue 2, pp. e0117744, (2016) (PubMed).
: "A nanoplasmonic biosensor for label-free multiplex detection of cancer biomarkers." in: Biosensors & bioelectronics, Vol. 74, pp. 341-346, (2015) (PubMed).
: "Multilayered, Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Formulations Suitable for Automated 3D High Throughput Drug Screening of Cancer-Stromal Cell Cocultures." in: Advanced healthcare materials, Vol. 4, Issue 11, pp. 1664-74, (2015) (PubMed).
: "MicroRNA expression signature of castration-resistant prostate cancer: the microRNA-221/222 cluster functions as a tumour suppressor and disease progression marker." in: British journal of cancer, Vol. 113, Issue 7, pp. 1055-65, (2015) (PubMed).
: "Measurement of serum prostate cancer markers using a nanopore thin film based optofluidic chip." in: Biosensors & bioelectronics, Vol. 77, pp. 491-8, (2015) (PubMed).
: "Suppression of CHK1 by ETS Family Members Promotes DNA Damage Response Bypass and Tumorigenesis." in: Cancer discovery, Vol. 5, Issue 5, pp. 550-63, (2015) (PubMed).
: "A nanowire-based label-free immunosensor: direct incorporation of a PSA antibody in electropolymerized polypyrrole." in: Biosensors & bioelectronics, Vol. 57, pp. 157-61, (2014) (PubMed).
Aliases for Prostate Specific Antigen 抗体
kallikrein related peptidase 3 (KLK3) 抗体kallikrein 3 (KLK3) 抗体
kallikrein 1-related peptidase C3 (Klk1c3) 抗体
kallikrein B, plasma 1 (Klkb1) 抗体
aminopeptidase puromycin sensitive (Npepps) 抗体
AAP-S 抗体
APS 抗体
goku 抗体
hK3 抗体
Kal-3 抗体
Kal3 抗体
Klk1c10l2 抗体
KLK2A1 抗体
KLK3 抗体
Klk3 抗体
MP100 抗体
PSA 抗体
Psa 抗体
R74825 抗体
rGK-3 抗体
RSGK-50 抗体
RSKG-50 抗体
您还需要查找其他产品吗?
- Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 (Prostaglandin G/H Synthase and Cyclooxygenase) 抗体
- Prostaglandin F2alpha 抗体
- Prostaglandin E Synthase 抗体
- Prostaglandin E Receptor 2 (Subtype EP2), 53kDa 抗体
- Prostaglandin D2 Receptor 2 抗体
- Prostacyclin Receptor 抗体
- PROSER1 抗体
- PROSC 抗体
- Prosaposin 抗体
- Propionyl CoA Carboxylase, alpha Polypeptide 抗体
- PROP1 抗体
- Prominin 2 抗体
- Proline Rich 15-Like 抗体
- Proline Rich 15 抗体
- Proline Rich 13 抗体
- Prolactin Receptor 抗体
- Prolactin 抗体
- PROL1 抗体
- Prokineticin Receptor 2 抗体
- Prokineticin Receptor 1 抗体
- Proteasome Subunit alpha 7 抗体
- Proteasome Subunit alpha 6 抗体
- Protein A 抗体
- Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1 抗体
- Protein B-Myc 抗体
- Protein G 抗体
- Protein Kinase C, beta 1 抗体
- Protein L 抗体
- Protein L-Myc 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase 1, Catalytic Subunit, alpha Isoform 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase 1, Regulatory Subunit 3B 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase 1, Regulatory Subunit 3C 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase 2, Regulatory Subunit B' alpha 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase 2, Regulatory Subunit B', delta 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase 2, Regulatory Subunit B', epsilon Isoform 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase 4, Regulatory Subunit 2 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ Dependent, 1A 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ Dependent, 1B 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ Dependent, 1D 抗体
- Protein Phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ Dependent, 1L 抗体




